Gallbladder Stone : Diagnosis and Treatment Methods - Assoc.Dr Mutlu Unver Izmir, Turkey
- Doç.Dr.Mutlu Ünver

- Apr 5, 2024
- 6 min read
Updated: Apr 13, 2024
What is the Gallbladder and Function?
The gallbladder is a pear-shaped organ located below the liver in the right upper abdomen. It is usually about 7 to 10 cm long and 4 cm wide. The main task of the gallbladder is to store and concentrate the bile fluid produced by the liver, which plays an important role in digestion.
The gallbladder stores bile fluid and condenses it at the same time. When food passes from our stomach into the small intestine, the gallbladder secretes bile fluid to facilitate digestion. Bile especially helps to digest fats. During the digestive process, bile breaks down and emulsifies fats, making digestion more effective.

The gallbladder plays an important role in the digestive system and stores, concentrates and secretes bile fluid, which helps to digest fats. This makes the digestive process more efficient.
How Gallbladder Stone Forms?
The formation of gallstones can be explained by the crystallisation process that occurs as a result of chemical changes in the bile fluid inside the gallbladder. These stones grow over time to form gallstones and can cause various health problems.
Why do gallbladder stones form?
The gallbladder is an important part of the digestive system and is vital for a healthy digestive process. However, many people with gallbladder problems may have difficulty recognising the symptoms of these problems.
First of all, let's examine the symptoms that you can easily recognise, starting with what the gallbladder is and how it works.
Gall Bladder: Function, Working Principle and Symptoms
The gallbladder, an important part of the digestive system, plays a critical role in our body's digestive process. However, most people have very little knowledge about the gallbladder. Here is what you need to know about what the gallbladder is, how it works and the symptoms of possible problems:
What are the main causes of gallbladder diseases?
Gallbladder disease can be the result of various nutritional, lifestyle and health factors. Let's take a look at the main causes of gallbladder disease.

Gallstones
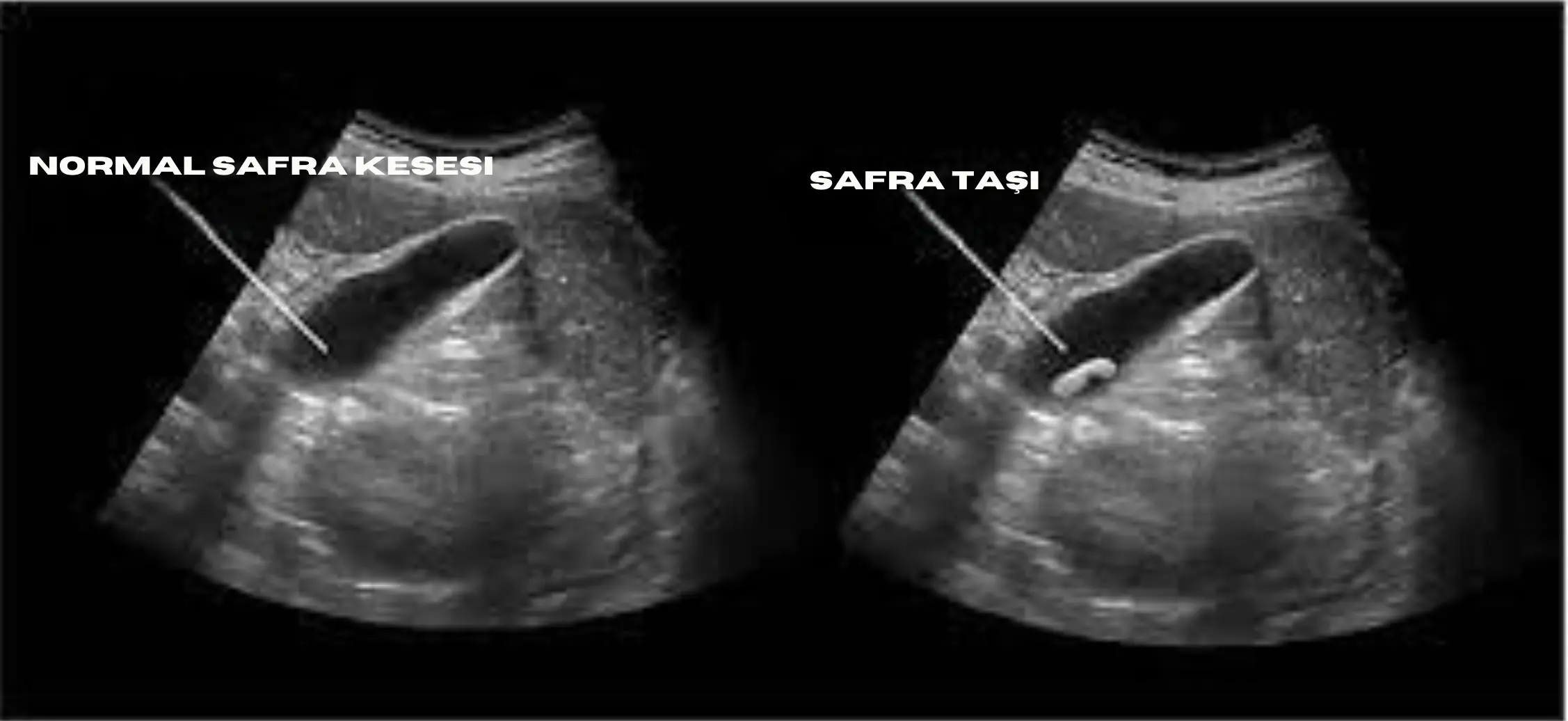
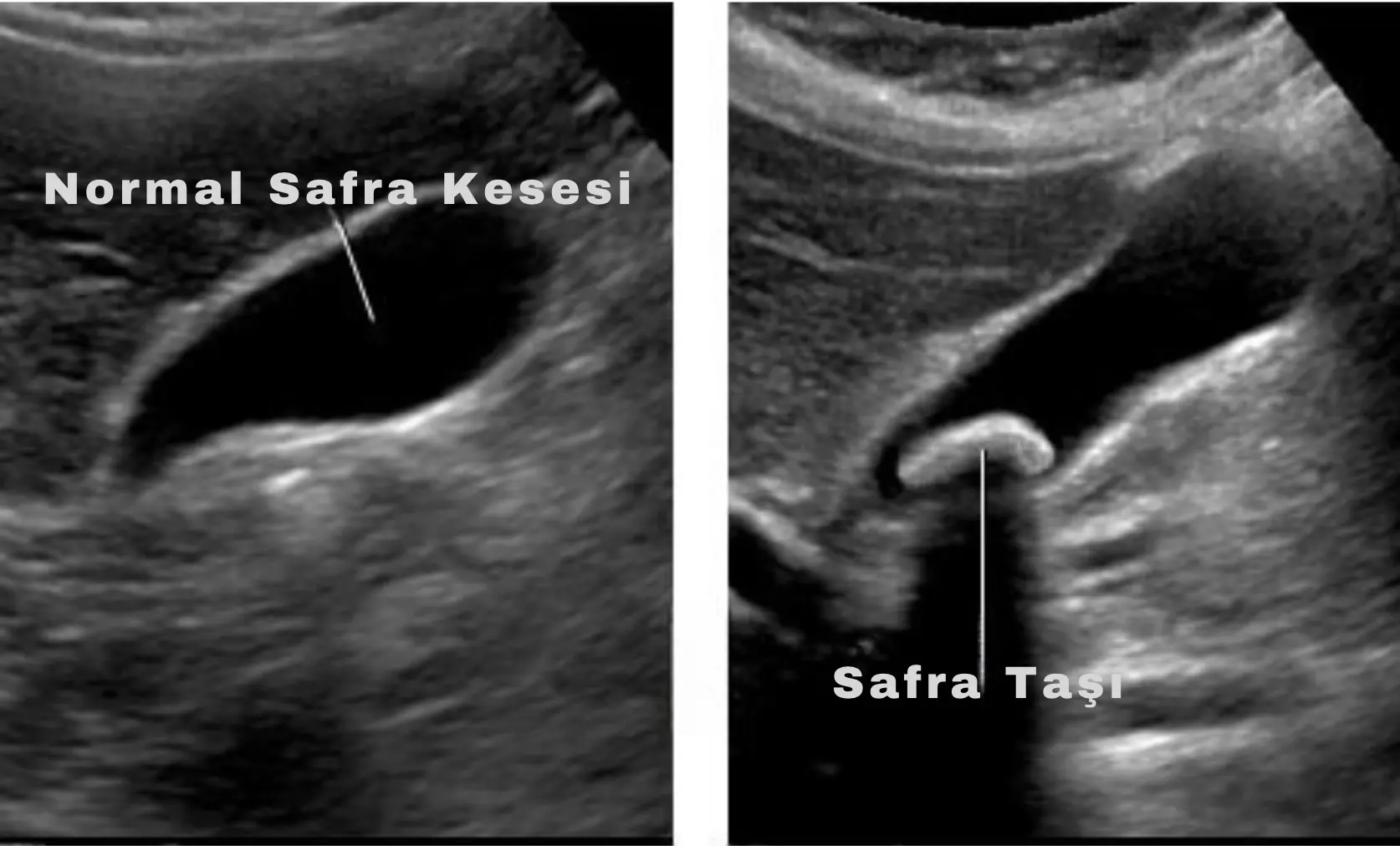
Gallstones form when substances in the bile fluid crystallise. These stones can accumulate inside the gallbladder and block the flow of bile or block the bile ducts, which can cause various gallbladder diseases. Gallstones can be of various sizes and sometimes do not cause symptoms, while in some cases they can lead to serious health problems.
Cholesterol Stones
These are stones formed due to high levels of cholesterol in the bile fluid. They are usually yellow in colour and make up the majority of gallstones.
Pigment Stones
These are stones formed by the accumulation of pigment substances such as bilirubin in the bile fluid. They are usually smaller in size and dark in colour.
Mixed Stones
These are stones formed by the accumulation of both cholesterol and pigment substances. These stones may have different components in the gallbladder.
Gallbladder Stone Diagnosis
To diagnose gallstones, doctors often use imaging tests. These may include:
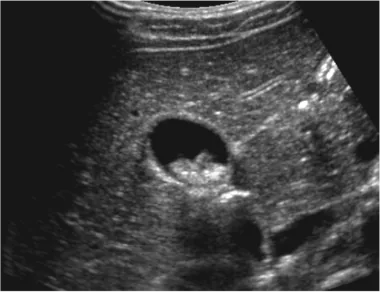
Ultrasonography (USG): This test is the most commonly used method to detect gallstones. Ultrasonography uses high-frequency sound waves in the body to visualise the gallbladder and surrounding structures. In this way, stones can be easily detected.
Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): These imaging tests can be used to assess the gallbladder and stones in more detail. However, they are generally not as widely preferred as ultrasonography.
Doctors also assess the patient's symptoms, especially pain in the right upper abdomen and digestive problems. These symptoms may be related to gallstones. However, imaging tests are usually needed to make a diagnosis.
Gallstones are usually diagnosed using imaging tests such as ultrasonography. Thanks to these tests, stones in the gallbladder can be easily detected and the treatment process can be started.
What are gallbladder polyps?
Gallbladder polyps are small abnormal tissue growths attached to a stalk on the inside of the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small organ that carries bile from the liver to the small intestine.
Prevalence: Gallbladder polyps are quite common.
Types: About 95 per cent are benign, i.e. non-cancerous polyps. However, 5 per cent can be malignant.
Size: Small polyps are usually between 1 and 1.5 cm. These are typically benign polyps and usually do not require treatment. However, polyps larger than 1 to 1.5 cm may be malignant and need to be treated.
Gallbladder polyps are usually benign and do not require treatment. However, as they increase in size, the risk of malignancy increases and treatment may be necessary. Therefore, polyps should be monitored regularly and treated if necessary.

Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment of Gallbladder Sludge
Gallbladder sludge is a condition caused by the thickening of bile that remains in the gallbladder for a long time. The gallbladder stores bile fluid produced by the liver. However, if the gallbladder is not emptied completely, sludge can form as a result of the accumulation of substances in it.
Symptoms: In some people, there may be no obvious symptoms despite the presence of gallbladder sludge. In this case, the person may not be aware of the disease for a long time. However, many patients may have obvious symptoms. These may include abdominal pain, especially a sharp pain under the right lower rib, chest and shoulder pain, nausea, vomiting and clay-like stools.
Diagnosis: Gallbladder sludge is usually diagnosed by imaging tests. Ultrasonography is the most commonly used method to detect thickened bile in the gallbladder.
Treatment: Most people with gallbladder sludge may not need treatment. However, if symptoms are severe or complications develop, doctors usually recommend removal of the gallbladder. This procedure can help relieve problems caused by gallbladder sludge.
Gallbladder sludge is a condition caused by thickening of bile that has accumulated in the gallbladder. Symptoms may or may not be obvious.
Gallbladder Inflammation
The medical term for inflammation of the gallbladder is "cholecystitis". This condition means that the gallbladder becomes inflamed. Gallbladder inflammation can occur in several different ways:
Acute Cholecystitis:
This condition usually occurs when a stone in the gallbladder becomes blocked. The blockage blocks the flow of bile and increases the pressure in the gallbladder, which causes inflammation. Acute cholecystitis may present with symptoms such as severe pain, fever, nausea and vomiting.
Chronic Cholecystitis:
Chronic cholecystitis is long-term low-grade inflammation. It usually develops as a result of gallstones or recurrent acute attacks. In chronic cholecystitis, symptoms may be milder and may include recurrent abdominal pain, indigestion and weakness.
Symptoms of gallbladder inflammation may include
Severe abdominal pain, especially in the upper right side
Fire
Nausea and vomiting
Abdominal tenderness and swelling
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Loss of appetite and fatigue
In case of suspected gallbladder inflammation, it is important to consult a doctor. Based on the symptoms, the doctor can perform a physical examination and, if necessary, order additional tests such as blood tests, ultrasound or other imaging tests.
Treatment can usually include controlling the inflammation with antibiotics and, if necessary, removal of the gallbladder.
Gallbladder Surgery
Gallbladder Stones (Cholelithiasis) Surgery:
It is a surgical procedure to remove the stones formed in the gallbladder.
The procedure called cholecystectomy is usually applied.
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is performed by placing a small camera and surgical instruments into the abdomen.
Gallbladder Stones in the Bile Duct (Choledocholithiasis) Surgery:
It is a surgical procedure performed to remove the stones formed in the bile duct and to open the duct.
Techniques such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and removal of stones can be used.
With endoscopic procedures, the stones are removed and the bile duct is opened.
Gallbladder Inflammation (Cholecystitis) Surgery:
It is a surgical procedure to solve problems caused by inflammation in the gallbladder.
Cholecystectomy can be applied.
The gallbladder is removed with laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Large Gallbladder Polyps Surgery:
It is a surgical procedure to remove large gallbladder polyps.
Cholecystectomy or open surgical methods can be used.
The gallbladder is removed together with the polyps.
What happens if the gallbladder stone is not removed?
Gallbladder Inflammation (Cholecystitis):
When gallstones get stuck in the gallbladder or block the ducts, they can cause inflammation of the gallbladder. This can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, fever and nausea.
Gallbladder Colic:
Gallstones can cause sudden and severe abdominal pain. These bouts of pain are called gallbladder colic and are often associated with movement or blockage of the stones.
Gallstone Pancreatitis:
Gallstones can cause inflammation of the pancreas by blocking the bile ducts. This can cause serious symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting and even jaundice.
Gallbladder Empyema:
Gallstones can increase the risk of infection in the gallbladder and cause inflammation within the gallbladder. This can lead to symptoms such as severe abdominal pain and fever.
Risk of Gallbladder Cancer:
Long-term gallstones can irritate the inner walls of the gallbladder, which can rarely increase the risk of gallbladder cancer.
If you experience any of these conditions, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. Because gallstones can lead to serious complications and require appropriate treatment.
Gallbladder Symptoms
Severe and sharp pain in the upper right abdomen:
Usually the most obvious symptom of gallbladder pain is a severe and sharp pain, especially in the upper right part of the abdomen. This pain usually occurs after eating or after consuming fatty foods.
The pain may radiate to your back or right shoulder:
Gallbladder pain can sometimes radiate to your back or right shoulder. This radiating pain is usually felt distinctly.
Nausea and vomiting:
Gallbladder pain can often be accompanied by nausea and even vomiting. These symptoms may be more pronounced, especially if the pain is severe.
Food intolerance:
People with gallbladder pain may find it difficult to digest food, especially fatty or heavy foods. They may therefore notice that their pain increases when they consume such foods.
Temporary relief:
People with gallbladder pain often notice that after a certain period of time their pain is relieved or gone. This is a period when the gallstones temporarily move or the gallbladder contracts.




















Comments